Commerce
Virtual Kitchens: How to Streamline Operations and Profit from Delivery-Only
August 12, 2020
Virtual kitchen companies are providing lower-risk solutions for restaurants to capitalize on online ordering and delivery demand.
As COVID-19 has altered the on-premise dining experience, it’s also influenced the demand for delivery. Because of this, technology has adapted to provide solutions for restaurants such as contactless dining for on-premise diners and online ordering systems for pickup and delivery. However, there is another solution for restaurants that are looking to capitalize on the online ordering demand and avoid the financial risk that comes with the traditional brick and mortar: virtual kitchens.
As a concept, virtual kitchens go by many names: ghost kitchens, dark restaurants, virtual brands, digital restaurants, virtual restaurants — the list goes on and on. Chances are if you’ve recently ordered delivery then you’ve ordered from one. So what are virtual kitchens and how can they benefit restaurant operators during COVID-19 and beyond?
Virtual kitchens are delivery-only restaurants that operate out of commercial kitchen spaces. These restaurants use third-party delivery services like Uber Eats, Grubhub and DoorDash to facilitate delivery. The New Yorker article, Our Ghost-Kitchen Future, put it best, ”The branding and food are real, but the restaurants do not exist elsewhere in the physical world.”
Consumers likely never know if the restaurant is virtual or not and do not have the option to walk up and order like one does for a food truck. Virtual kitchens are simple to set up with much less red-tape, have lower operational costs and provide a greater level of safety for diners and staff during COVID-19. Because of these obvious benefits and the exponential increase in demand for delivery, venture capitalists have flocked at the opportunity to own a piece of the market share and have invested in scalable incubators for new virtual restaurants.

Virtual Kitchens are On The Rise
In 2019 alone, $2.9 billion was poured into U.S. virtual kitchen companies. This has been fueled by the projection that the online food delivery market is expected to be a $1 trillion opportunity globally by 2030. COVID-19 has directly influenced this growth, shifting consumer habits overnight and leaving restaurants to adapt operations for takeout and delivery.
Virtual kitchen companies are acting quickly to capitalize on the $800 billion a year restaurant industry. Their reasoning, if more kitchen space is needed to keep up with demand, why not build it? There are several types of virtual kitchen concepts that are emerging.
Types of Virtual Kitchen Concepts
Incubators or Pop-Up Kitchens
These kitchens are small extensions attached to a traditional brick and mortar restaurant and are only used for fulfilling online orders and deliveries. These are useful for restaurants looking to test a new concept or cuisine as well as to meet the burgeoning demand for delivery. Restaurants who are adapting to delivery because of COVID-19 can benefit from this type of kitchen model, especially as they look to reopen to on-premise diners.
Commissary or Shared Kitchens
In this model, multiple restaurants share kitchen space, appliances and tools. These are the most common type of turn-key model (once rented, the restaurant takes over operations) of the majority of virtual kitchen companies. Companies like Kitchen United and Virtual Kitchen co., support local restaurants by providing clean, safe, state-of-the-art kitchen facilities that streamline operations. Virtual kitchens can open up anywhere where demand for delivery is needed, providing greater reach to a restaurant’s consumers and the convenience of choice for those same consumers.
These kitchen concepts greatly benefit the logistics and supply chain as well. New virtual restaurants pop up every day providing more business opportunities for kitchen equipment suppliers and foodservice distributors like US Foods. Because of this, they’ve become increasingly ingrained into the bigger economic fabric — all but solidifying their place and influence in the restaurant industry as a whole. Ghost kitchens are also a product of the new gig economy which has given rise to more delivery couriers to meet consumer demand.
The Benefits of Operating a Virtual Restaurant
Avoid High Opening Costs
Virtual restaurant companies invest in real estate and build out commercial kitchens that can be rented. These delivery-only restaurants operate in the same facility as others, essentially eliminating many of the high opening costs that traditional brick and mortar restaurants pay. These costs include the various permits and certifications restaurants must have before starting construction and opening their doors. Traditional restaurants can sometimes spend months waiting on the state and local governmental approvals and permits, paying costly rents with zero income. Virtual restaurants bypass many of the traditional overhead costs.
Test Concepts, Brands and Trends
Virtual restaurants are a great way to test an existing concept or brand in a new market. For brands that have already established a following in a select market, virtual restaurants are an easy testing ground for new or expanded menu items in the brick and mortar. Restaurants could also use the opportunity to focus in on a specific menu item and test for expansion.
In the food world, trends develop that can send popular items or cuisines to permeate popular culture. These changes in food, dining, or concept preferences shape how restaurants operate and what they offer and can be either short-lived or have a lasting impact on the industry. Virtual restaurants are a way for restaurants to capitalize on a trending ingredient or concept with relatively lower risk.
Expand Concepts with Less Financial Risk
Because of lower financial and operational risk, the opportunity for a restaurant to operate in a city or market that previously wasn’t financially viable is now more accessible. This opens possibilities for many small businesses to offer their cuisine to larger audiences and grow their business.
Poulet Sans Tête is the sister restaurant to Left Bank in New York City. They also operate in the same facility and are only available for delivery. This is an example of how a concept can operate online for delivery with less operational risk and overhead costs. Restaurants can similarly test the market and if there is a demand for the offerings, then operators can choose to open a brick and mortar experience down the line.

Streamline Operations Through Direct Online Ordering
Virtual kitchen companies make it easy for restaurants to get started in their new space. Then, it’s up to the restaurant to facilitate delivery operations. Before they can begin, virtual restaurants must first decide how guests will order online and what type of delivery fulfillment service to partner with. There are two options: direct online ordering or third-party marketplaces. With the latter, virtual restaurants are still subject to the disadvantages that come with third-party marketplaces like Uber Eats and Grubhub such as high-commission fees on each order placed, which is detrimental to any restaurant’s bottom line.
Restaurants with a strong following should consider a direct online ordering system to streamline online orders and delivery fulfillment.
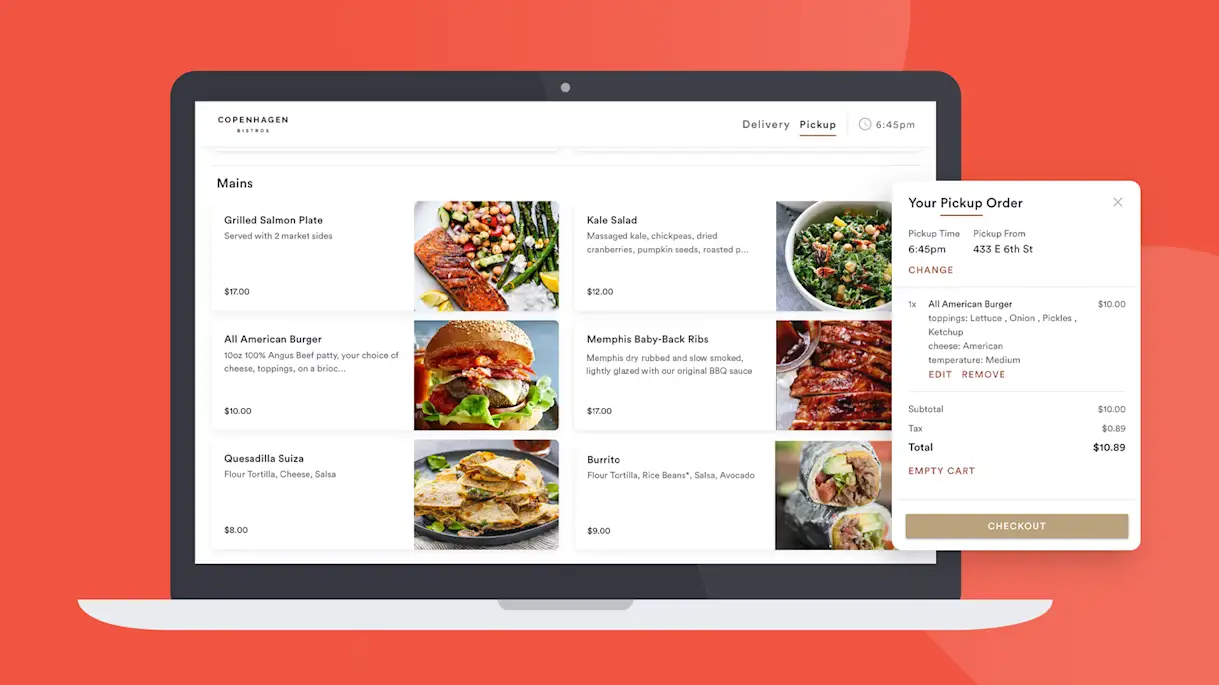
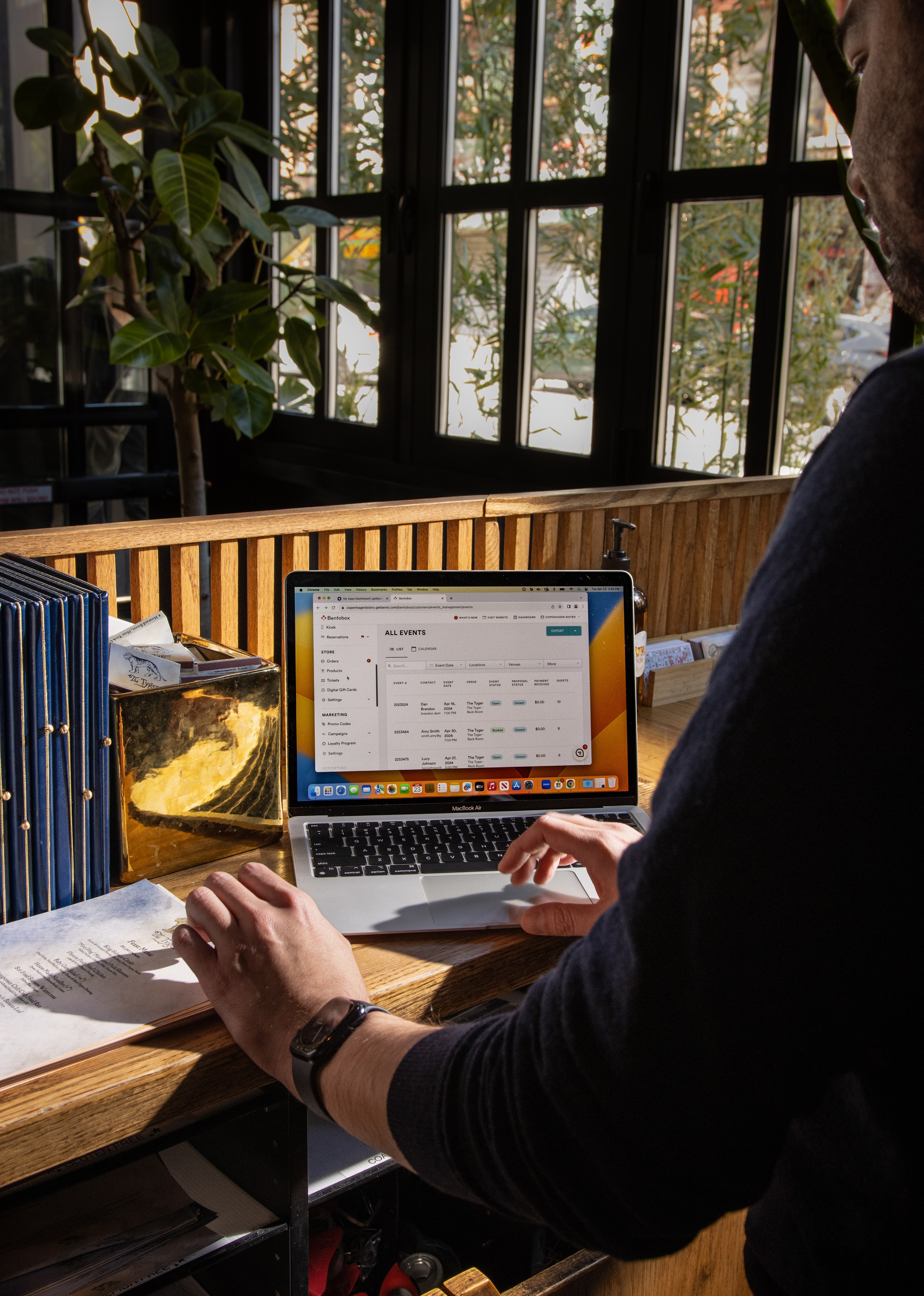
Direct online ordering systems, like Bento Ordering, allow visitors to place orders for delivery through the restaurant’s website. It’s an all-in-one-system to maximize profits with zero-commission fees involved and promotes brand loyalty. This is particularly useful for restaurants who have a ghost-kitchen extension to their brick and mortar that fields online orders for delivery.
Direct online ordering systems also provide insightful data to restaurants in real-time. Restaurants can calculate average order volume, order size and see their weekly number of visitors. With this data, restaurants can forecast weekly and monthly sales to build accurate budgets, make financial decisions, save on supplies and reduce food waste.
During COVID-19, Safety is Key
As the rise in COVID-19 cases continues throughout the nation, reopening procedures are increasingly becoming more difficult for restaurants. Keeping guests and staff safe is an important part of restarting operations. With zero space for diners, smaller staff, and the elimination of high-touch points, virtual restaurants provide a higher level of safety for all parties involved. Also, operators can maintain strict cleaning and safety procedures with more efficiency.

What’s Next for Virtual Kitchens?
As COVID-19 continues to impact restaurants across the nation, new technologies and solutions are helping restaurants adapt in a rapidly-changing environment. This includes virtual kitchen companies who are making great strides in helping restaurants. And with COVID-19, they’ve become less of an option and more of a necessity for many restaurants. Their relatively low overhead-risk makes them particularly appealing, especially from a health perspective. And in a new normal, riddled with uncertainty, virtual restaurants provide operators with the opportunity to grow their brand by testing new markets, new offerings and streamlining operations to further save money and reduce costs.

BentoBox Marketing & Commerce Platform
Want to stand out online? Let's chat.
Drive revenue directly through your website.
Recommended
BentoBox News
BentoBox Launches Online Ordering for Restaurants
February 5, 2020
New online ordering platform puts restaurants back in control and lets consumers order directly from restaurant websites.
BentoBox News
Introducing Dine-In Order & Pay: Paperless Menus and Payment for Restaurants
August 5, 2020
How Dine-In Order & Pay by BentoBox changes the game for restaurants.

Design Inspiration
The 20 Best Restaurant Websites of 2024
January 3, 2023
Our annual roundup of the internet's best restaurant websites.

